| Panel |
|---|
| Section |
|---|
| Column |
|---|
| 
| Info |
|---|
In short, once you have realised this plot, you will have understood and used the main concepts of Magic |
|
|
|
Before you start ...
During this tutorial, you will use Python and Magics++ on a Linux workstation.
Here is a list of basic commands you may want to use.
Basic UNIX commands:
- ls : list the files in the current directory
- mkdir my_exercise : create a directory called my_excercise
- cd my_exercise : go to the directory my_excercise. my_excercise becomes the current directory
Using an editor:
There are several editors available
- vi
- emacs
- kate
- nedit
- geany ( Python syntax highlighted..)
Run the python interpretor :
In this tutorial we are expecting you to create a python script using your favourite editor and run python to interpret it. Your system have been set-up already and you can use Magics and python by typing the single command:
python magics.py
Visualise your result:
Magics will generate a Postscript or a PNG output. To visualise the results, you can use one of the following commands:
- gv magics.ps : visualise a Postscript file called magics.ps
- display magics.png : visualise a PNG file called magics.png
- xv magics.png : visualise a PNG file called magics.png
First Step - warming up : the "Hello World" example
| Panel |
|---|
|
| Section |
|---|
| Column |
|---|
| Get familiar with the environment Find your favourite editor to edit your Python script Create your first Magics script Learn how to: - Run your script
- See your results
- Modify your script
|
| Column |
|---|
| 
|
|
|
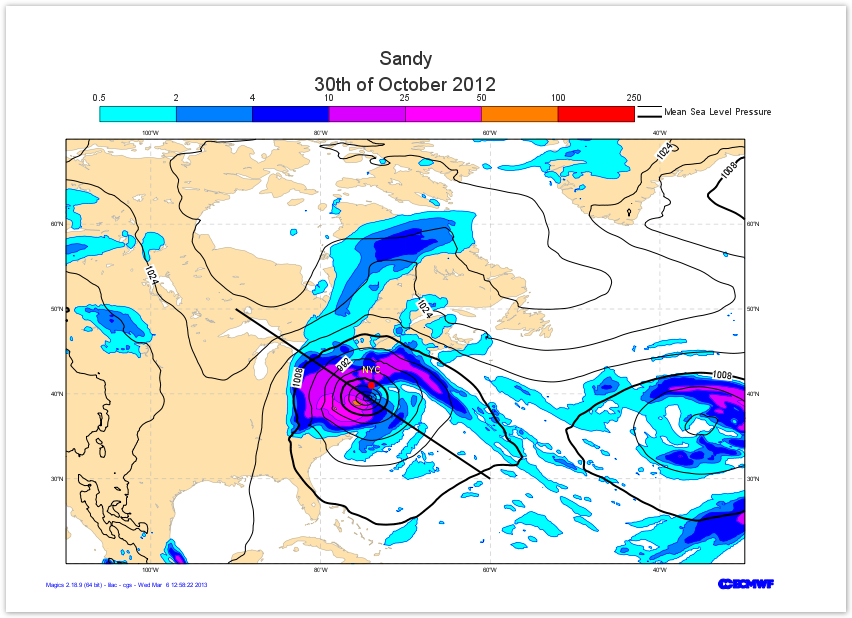
Second Step - a geographical map
| Panel |
|---|
|
| Section |
|---|
| Column |
|---|
| 
|
|
|
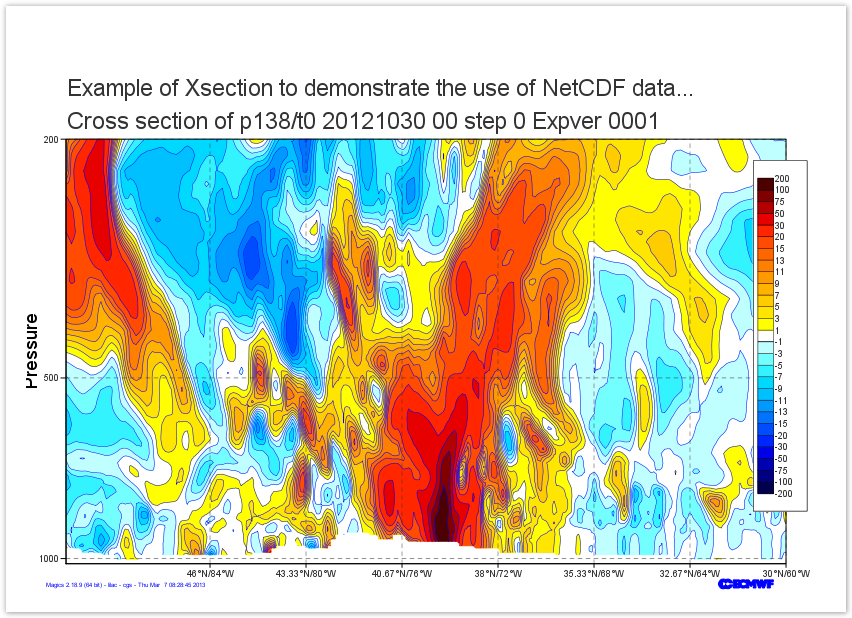
Third Step - a Cross Section
| Panel |
|---|
|
| Section |
|---|
| Column |
|---|
| 
|
|
|
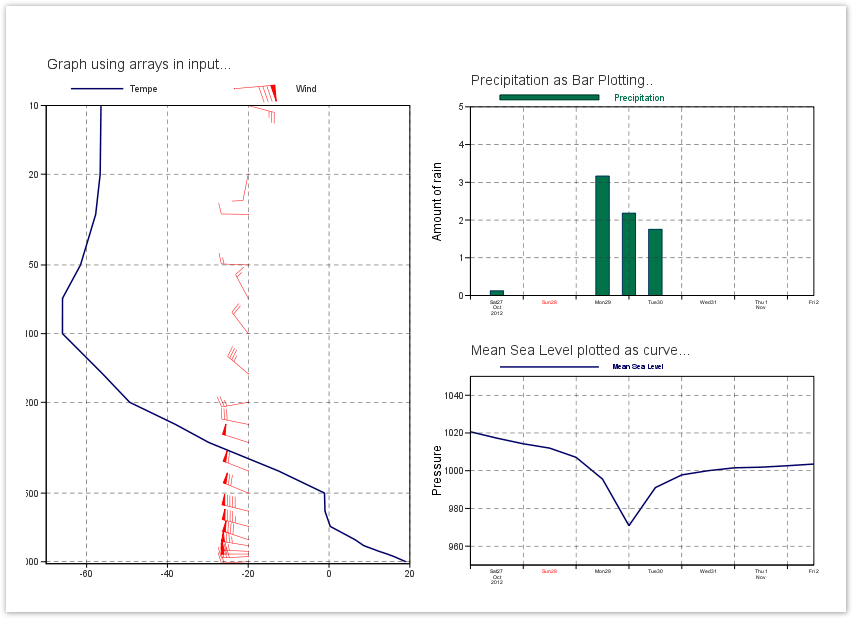
Fourth Step - a vertical profile and a Time serie
| Panel |
|---|
|
| Section |
|---|
| Column |
|---|
| 
|
|
|
Fifth Step - More on Symbol Plotting
| Panel |
|---|
|
| Section |
|---|
| Column |
|---|
|
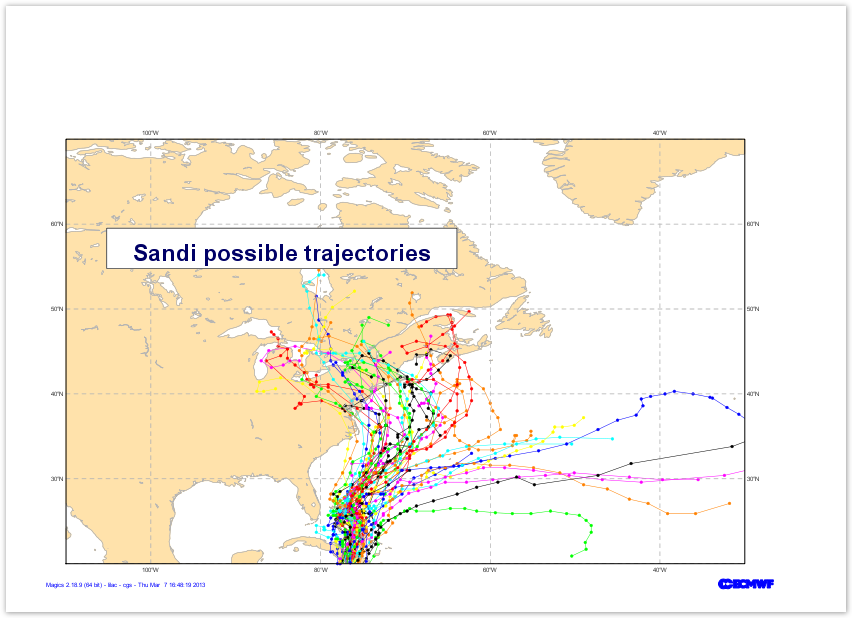
Learn how to - Create a long list of visualisation
- Load and use CSV files
Go to Tutorial... |
| Column |
|---|
| 
|
|
|
Finally - a complex layout
| Panel |
|---|
|
| Section |
|---|
| Column |
|---|
| - Create a complex layout to put all these maps together
- Understand the notion of page and sub page
Go to Tutorial... |
| Column |
|---|
| 
|
|
|
Download the full solution ...





