| Panel |
|---|
| title | Visualising ODB in Magics |
|---|
|
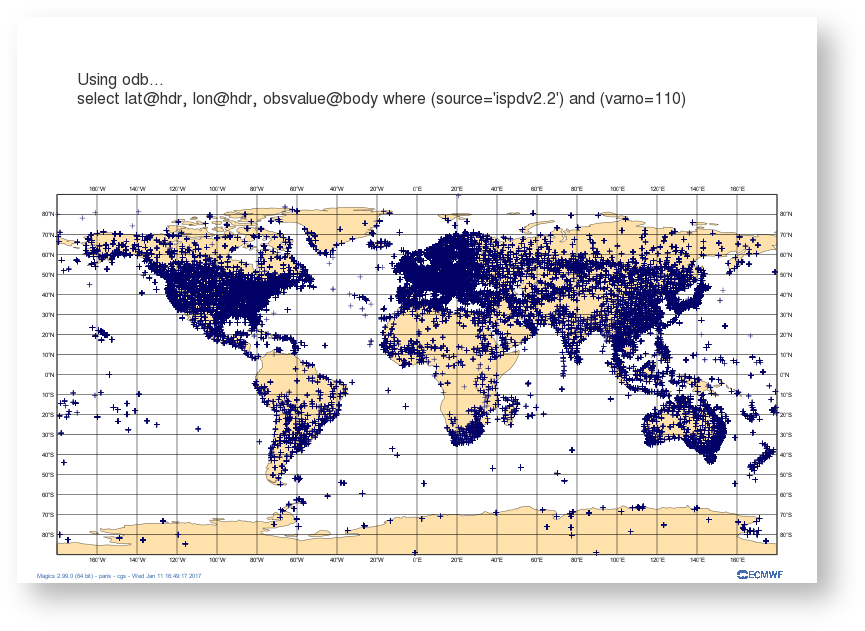
There are several ways on visualisating ODB data in Magics. - use the ODB Magics objects. This allows Magics to read a odb file and extract some columns for geographical plots or graph.
- In python, it also possible to use odb_api packages to create a numpy array and pass the values in memeoty to Magics. magics is then able to perform symbol plotting on a geographical area, time series, etc ..
This page presents examples of these different plottingsvisualisation, and offers skeletons of python programs. |
...
To run the example at ECMWF:
- download python scripts and data
- module load Magics/new
- module load odb_api
toc
Using an ODB file and create a geographical map
...
| Section |
|---|
| Column |
|---|
| 
|
| Column |
|---|
| | Code Block |
|---|
| language | py |
|---|
| title | Simple symbol plotting |
|---|
| collapse | true |
|---|
| # importing Magics module
from Magics.macro import *
# Setting of the output file name
output = output(output_formats=['png'],
output_name_first_page_number='off',
output_name="odb_step1")
# Background Coastlines
background = mcoast(
map_coastline_sea_shade_colour='white',
map_coastline_land_shade_colour='cream',
map_grid='on',
map_coastline_land_shade='on',
map_coastline_sea_shade='on',
map_label='on',
map_coastline_colour='tan',
)
# Import odb data
odb = odb_geopoints(odb_filename='geo.odb',
odb_latitude_variable='lat@hdr',
odb_longitude_variable='lon@hdr',
)
# Define the symbol plotting
symbol = msymb(symbol_type='marker',
symbol_colour='navy',
symbol_marker_index=3,
symbol_height=0.4,
)
# Add a title
lines = ['Using odb...',
'select lat@hdr, lon@hdr, obsvalue@body where (source=\'ispdv2.2\') and (varno=110)',
]
title = mtext(
text_lines=lines,
text_justification='left',
text_font_size=0.7,
text_colour='charcoal',
)
#Create the plot
plot(output, background, odb, symbol, title)
|
|
|
Now, we are going to colour the symbol according to the value of the observation. The advanced mode for symbol plotting offers an easy way to specify range and colours, we add a legend for readability.
| Section |
|---|
| Column |
|---|
| 
|
| Column |
|---|
| | Code Block |
|---|
| language | py |
|---|
| title | Advanced symbol plotting |
|---|
| collapse | true |
|---|
| # importing Magics module
from Magics.macro import *
# Setting of the output file name
output = output(output_formats=['png'],
output_name_first_page_number='off',
output_name='odb_step2')
# Background Coastlines
background = mcoast(
map_coastline_sea_shade_colour='white',
map_coastline_land_shade_colour='cream',
map_grid='on',
map_coastline_land_shade='on',
map_coastline_sea_shade='on',
map_label='on',
map_coastline_colour='tan',
)
# Import odb data
odb = odb_geopoints(odb_filename='geo.odb',
odb_latitude_variable='lat@hdr',
odb_longitude_variable='lon@hdr',
odb_value_variable='obsvalue@body',
)
# Define the symbol plotting
symbol = msymb(symbol_type='marker',
symbol_colour='navy',
symbol_advanced_table_selection_type='list',
symbol_advanced_table_level_list=[50000., 75000., 90000., 100000.,
100500., 101000., 101500., 102000., 102500., 103000.,
103500., 104000., 105000.],
symbol_advanced_table_min_level_colour='blue',
symbol_advanced_table_max_level_colour='red',
symbol_advanced_table_colour_direction='clockwise',
symbol_table_mode='advanced',
legend='on'
)
#Adding some text
lines = ['Using odb colouring the sumbol according to the value of the observation...',
'select lat@hdr, lon@hdr, obsvalue@body where (source=\'ispdv2.2\') and (varno=110)',]
title = mtext(
text_lines=lines,
text_html='true',
text_justification='left',
text_font_size=0.7,
text_colour='charcoal',
)
#adding some legend
legend = mlegend(legend='on', legend_text_colour='navy',
legend_display_type='continuous')
#Create the plot
plot(output, background, odb, symbol, title,legend)
|
|
|
Loading the data into a numpy array and passing them to Magics
...
| Section |
|---|
| Column |
|---|
| 
|
| Column |
|---|
| | Code Block |
|---|
| language | py |
|---|
| title | Using numpy array |
|---|
| collapse | true |
|---|
|
# importing Magics module
from Magics.macro import *
#Loading ODB in a numpy array
import odb
import numpy
import datetime
odb = numpy.array([r[:] for r in
odb.sql("select lat@hdr, lon@hdr, obsvalue@body from '%s'"
% 'geo.odb')])
lat = odb[:, 0]
lon = odb[:, 1]
#Here we convert the values from Pascal to HectoPascal.
values = odb[:, 2]/100
# Setting of the output file name
output = output(output_formats=['png'],
output_name_first_page_number='off',
output_name='odb_step3')
# Background Coastlines
background = mcoast(
map_coastline_sea_shade_colour='white',
map_coastline_land_shade_colour='cream',
map_grid='on',
map_coastline_land_shade='on',
map_coastline_sea_shade='on',
map_label='on',
map_coastline_colour='tan',
)
#Set the input data
input = minput(input_latitude_values=lat,
input_longitude_values=lon,
input_values=values)
# Define the symbol plotting
symbol = msymb(symbol_type='marker',
symbol_colour='navy',
symbol_advanced_table_selection_type='interval',
symbol_advanced_table_interval=5.,
symbol_advanced_table_min_level_colour='blue',
symbol_advanced_table_max_level_colour='red',
symbol_advanced_table_colour_direction='clockwise',
symbol_table_mode='advanced',
legend='on'
)
#Adding some text
lines = ['Using odb colouring the sumbol according to the value of the observation...', "select lat@hdr, lon@hdr, obsvalue@body where (source='ispdv2.2') and (varno=110)",
'<magics_title/>']
title = mtext(
text_lines=lines,
text_html='true',
text_justification='left',
text_font_size=0.7,
text_colour='charcoal',
)
#adding some legend
legend = mlegend(legend='on', legend_text_colour='navy',
legend_display_type='histogram',
legend_label_frequency=5)
#Create the plot
plot(output, background, input, symbol, title,legend)
|
|
|
Creating a time series from an ODB data.
...
Note the use of axis_type = 'date', axis_date_type = "automatic" in the setting of the horizontal axis. This is a nice feature of Magics that will adjust the labels to show hours, days, months or years according to the length of the time series.
Now we will add the data. The file count.odb contains the following information.
...
Note that we have now set subpage_x_axis_type to regular and subpage_x_automatic = on. This will not interpret the date as a date but as a integer, and will use the min and max of the data to setup the limits of the projection. It is not the plot we really want, but it shows quickly your data. gives a quick overview.
Let's nterpret Now we will interpret the date as date, and the time series should be fine.
| Section |
|---|
| Column |
|---|
| 
|
| Column |
|---|
| | Code Block |
|---|
| language | py |
|---|
| title | Interpreting the date |
|---|
| collapse | true |
|---|
| # importing Magics module
import Magics.macro as magics
#First we read the ODB in a numpay array
# importing ODB
import odb
import numpy
import datetime
odb = numpy.array([r[:] for r in
odb.sql("select date@hdr, series from '%s'"
% 'count.odb')])
dates = odb[:, 0]
count = odb[:, 1]
#Now we convert the date to the ISO date Format that Magics can understand.
dates = map(lambda x : datetime.datetime.strptime("%s" % x, "%Y%m%d.0"), dates)
dates = map(lambda x : x.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M"), dates)
# Setting of the output file name
output = magics.output(output_formats=['png'],
output_name_first_page_number='off',
output_name='odb_graph3')
# Define the cartesian projection
map = magics.mmap(subpage_map_projection = "cartesian",
subpage_x_axis_type = 'date',
subpage_y_axis_type = 'regular',
subpage_x_automatic = 'on',
subpage_y_automatic = 'on',
)
#define the axis
horizontal_axis = magics.maxis(axis_orientation = "horizontal",
axis_type = 'date',
axis_date_type = "automatic",
axis_grid = "on",
axis_grid_line_style = "solid",
axis_grid_thickness = 1,
axis_grid_colour = "grey",
axis_minor_tick ='on',
axis_minor_grid ='on',
axis_minor_grid_line_style = "dot",
axis_minor_grid_colour = "grey",
axis_title = 'on',
axis_title_text = "Time...",
)
vertical_axis = magics.maxis(axis_orientation = "vertical",
axis_grid = "on",
axis_grid_line_style = "solid",
axis_grid_thickness = 1,
axis_grid_colour = "grey",
)
data = magics.minput(input_x_type = "date",
input_date_x_values = dates,
input_y_values = count
)
graph = magics.mgraph(graph_line_colour="evergreen")
#Add a text
title = magics.mtext(text_lines=['Adding the data to the time series'])
# Execute the plot.
magics.plot(output, map, horizontal_axis, vertical_axis, data, graph, title)
|
|
|
In the example we are using numpy array to manipulate the ODB, this gives all the computations facilities. Once done, the result can just be passed to Magics using through a numpy array.



