...
| Warning | ||
|---|---|---|
The new MARS client with the MIR interpolation library is currently in BETA, and it is meant for tests only. Do not use it for any operational purpose. You can try the new MIR-enabled MARS client on any ECMWF computing platform with:
You are encouraged to test this new version of the MARS client and report any issues to advisory@ecmwf.int . Testing MARS/MIR through the ECMWF WebAPI will also be possible soon. |
MIR stands for Meteorological Interpolation and Regridding and is a library of routines for interpolation and regridding of meteorological fields. This new piece of software is replacing the veteran EMOSLIB when it comes to perform those operations in MARS. Beyond this, MIR’s flexible design facilitates scalability improvements and additional features. These include efficiency gains, a high degree of user configurability, and support for a wider range of grids than in the current package. See the related article in the ECMWF newsletter no.152 for a more complete description of this new library.
| Table of Contents |
|---|
Important dates
- June 2018: Release of a MARS/MIR which will be considered ready for production. The old MARS/EMOSLIB client would still be the default.
- Autumn 2018: MARS/MIR becomes the default version at ECMWF. The old MARS/EMOSLIB would still be accessible, but there will be no further updates to it.
The exact dates for each milestone will be communicated closer to their times.
Questions and Answers
| Expand | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
The EMOSLIB interpolation package was written in the 1980s and much has changed since then: the model grid resolution has steadily increased, a variety of grid types have been introduced, and many new parameters have been added over the years, often associated with different processing requirements. Both software and hardware technologies, such as programming languages, design paradigms, supporting libraries and hardware architectures, have evolved significantly. These aspects, together with new numerical methods and ECMWF's improved understanding of user requirements, have prompted ECMWF to design the new, extensible and easy-to-maintain MIR package |
...
| Expand | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
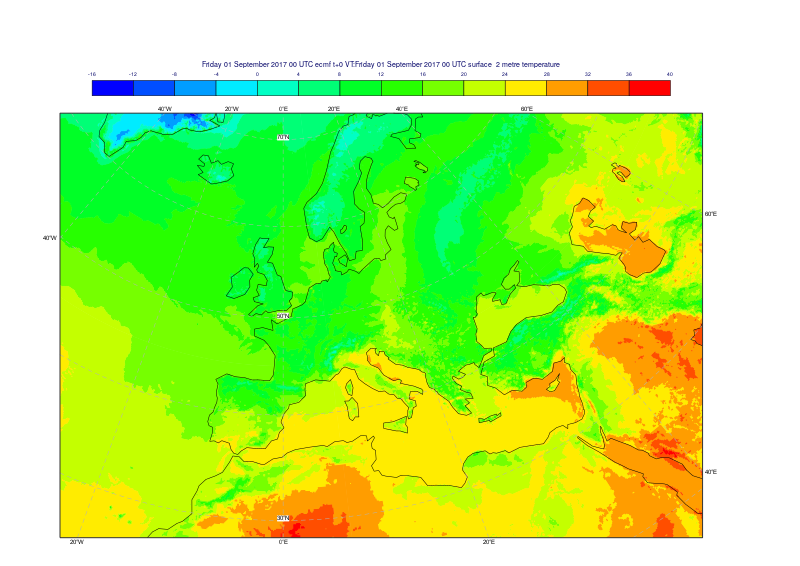
MIR has undergone a thorough validation process and tests to ensure its quality and correctness. However, since the implementations and strategies used in both packages are different, you may see some differences when using MIR instead of EMOSLIB. How significant those differences will be will depend on each specific case. Here is an example. The same 2m temperature field on a native O1280 grid has been interpolated to a 0.1/0.1 latitude-longitude grid using both methods. Plots have been produced for both, together with a third one with the differences greater than half a degree Celsius between them.
|
| Expand | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
At the moment MIR is only made available through the MARS client. In the medium term, a standalone command line tool based on MIR may become available. Other release options may also be considered in the future. |
Highlights and main differences
...
| Info | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
| Unlike EMOSLIB, MIR does not use any special processing for precipitation fields. |
...
Subareas
MIR brings a number of improvements in the sub-area subarea and cropping operations.
Consistency with fields from dissemination
...
Subareas of reduced Gaussian grids
EMOSLIB only supports sub-area subarea operations on regular Gaussian or lat-lon grids. MIR is capable of cropping sub-areas subareas and frames directly from global reduced Gaussian grids, including the octahedral reduced Gaussian grid.
...
MIR is providing different values at the poles to those obtained with EMOSLIB for interpolations to regular latitude-longitude grids which include points at latitudes 90ºN or 90ºS.
Known Issues
RESOL=AV uses wrong intermediate Gaussian grid
When using RESOL=AV and transforming from spectral to grid, the corresponding intermediate Gaussian grid to be used should be the cubic reduced Gaussian grid by default (i.e., O = T+1), as described above. However, at this point MIR uses a full (regular) gaussian grid with linear truncation (i.e., F = (T+1)/2).
| Info |
|---|
This issue has been resolved in a version of the MARS client using MIR (version 0.8.5) released on 14 November 2017. |
Winds on rotated grids
There are known issues with wind fields when working with rotated grids. In particular, wind speeds are correct but the direction is wrong due to a problem in computing the angles.
| Info |
|---|
This issue has been resolved in a version of the MARS client using MIR (version 0.8.5) released on 14 November 2017. |
Performance for small subareas
See Resolved Issues in MARS/MIR for those issues which have been fixed.
Performance for subareas
When defining certain When defining small subareas, MIR tends to be slower compared to EMOSLIB. At the moment, MIR does the interpolation on a global grid and performs the cropping operation later, whereas EMOSLIB will only interpolate on the subarea defined. This may be optimised in future versions.
...