| Scroll pdf ignore | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
Case description
In this exercise we will use Metview to explore the various ways ensemble forecast forecasts can be processed and visualised. The case we will investigate is related to a low pressure system crossing the UK on 10 August 2014: it caused high winds and heavy rain especially in the South-Western part of the country. The system has picked up moisture and energy left over from Hurricane Bertha on the other side of the Atlantic.
The first three plots show the precipitation forecast for the period of August 24 00UTC - 25 00UTC from various model runs preceding the event by 1, 3 and 5 days, respectively. The last plot shows the observed rainfall for the same period.
We will use both Macro and icons to ....
XXX Download data
Verify that the data are as expected.
Remember to give your icons useful names!
Evaluating the forecasts
In this part of the exercise we will create the plot shown below:
In this plot each map contains various forecasts for the maximum 10 m wind gust in a 6-hour period:
- top left: the latest forecast before the event
- top right: the forecast run 4 days before the event
- bottom left: the ensemble mean for the ENS forecast run 4 days before the event
- bottom right: the ensemble spread for the ENS forecasts run 4 days before the event
Setting the
...
View
With a new Geographical View icon, set up a cylindrical projection with its area defined as
| Code Block |
|---|
South/West/North/East: 43/-20/60/10 |
Set up a new Coastlines icon with the following:
- the land coloured in cream
- the coastlines thick black
- use grey grid lines at every 5 degrees.
Seeing what happened
...
- .
...
Part 1: Checking the forecast
...
Defining the layout
With a new Display Window icon define a 2x2 layout so that each plot should contain your view.
Visualising the latest forecast
The GRIB file fc_latest_oper.grib contains the latest forecast run preceding the event. Drag it into the top left map and customise it with the wgust_shade Contouring icon and the title_oper Text Plotting icon. Animate through the fields to see the location of the areas heavily hit by the storm.
Visualising the operational forecast
The GRIB file fc_oper.grib contains the operational forecast run at 7 August 00 TC UTC (four 4 days before the event). Drag it into the top right map and customise it in the same way as the previous plot. You will see that the wind storm was not present in the forecast.
Visualising the ensemble mean
The GRIB file fc_pfens.grib contains the control forecast member and the 50 perturbed forecast member members of the ENS run at 7 August 00 TC UTC (four 4 days before the event). We will write a macro to compute and visualise the mean of these the ensemble members using a Macro.
So create Create a new Macro and edit it. First, read the GRIB file in:
| Code Block |
|---|
g=read("fc_pfens.grib") |
Since this Our GRIB contains several three time steps we need to write a loop (78, 84 and 90 hours, respectively) and we would like to compute the ensemble mean for each time step individuallyone separately. To achieve this goal we will write a loop going through the time steps. First, define the fieldset that will contain the resulting means:results
| Code Block |
|---|
e_mean=nil |
We will process the fields in a loop going through Next, add this piece of code to define the loop (we store the time steps in a list):
| Code Block |
|---|
tsLst=[78,84,90,96] loop step in tsLst ...your code will go here ... end loop |
Within the loop, first, read all the 51 ENS members for the given timesteptime step:
| Code Block |
|---|
f=read(data: g, step: step ) |
Next, compute the probability in as followstheir mean with the mean() macro function:
| Code Block |
|---|
f =f > val f=100*mean(f) |
In t
Last, add it this field to the resulting fieldset:
| Code Block |
|---|
e_probmean = e_probmean & f |
By doing so the loop's body is completed. We finish the macro by returning the resulting fieldset:
| Code Block |
|---|
return e_probmean |
| Info |
|---|
By using the |
Drag it your Macro into the bottom left map and customise it with the probwgust_shade Contouring icon and the title_prob Text Plotting icon. You will see icon. You would also need a custom Text Plotting icon for the title. Take a copy of the one used for the previous plots (called title_oper) and tailor it to your needs. When you analyse the plot you will notice that the ensemble mean hints that high wind speed can happenfor higher wind gusts in our area of interest.
Visualising the ensemble spread
The ensemble spread is the standard deviation of the perturbed forecast ENS members. You We can compute it in a very similar way to the ensemble mean. The only difference is that this time you we need to use the stdev() function instead of mean(). Now do it.Drag it is your task to write a Macro for it. Once you finished your Macro drag it into the bottom right map and customise it with the wgust_spread_shade Contouring icon and the spread_mean with a custom Text Plotting icon. . You will see that the ensemble ....
Part 2: checking the probabilities
spread is fairly high in the investigated area.
Checking the probabilities
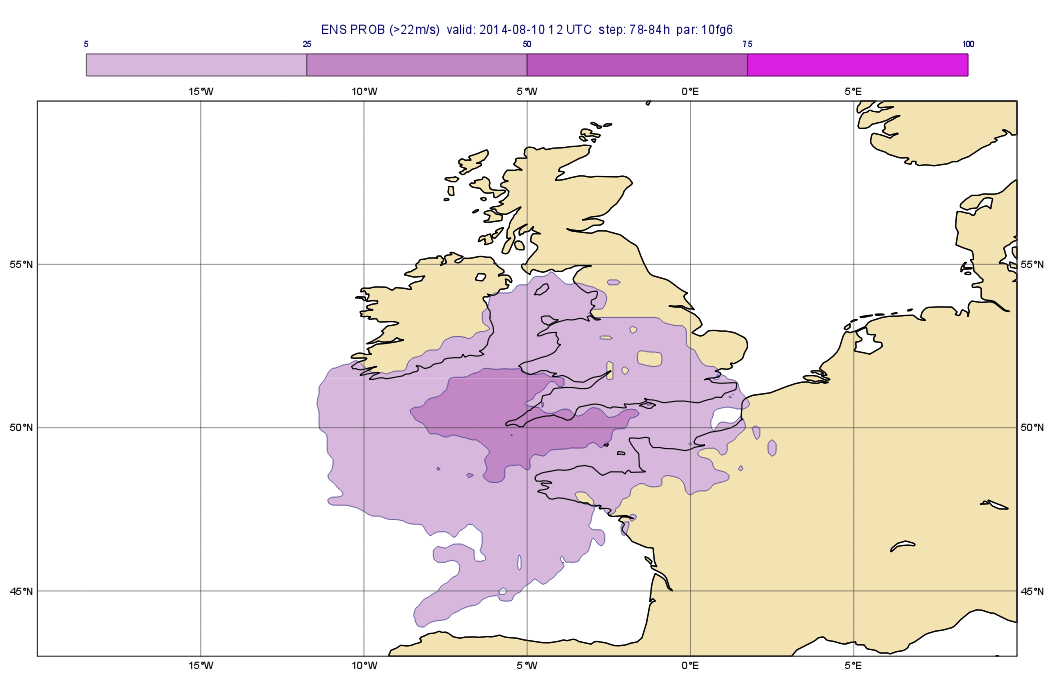
In this part we will The next step is to estimate the risk of the wind gust being higher than certain thresholds: i.e. we will compute some probabilities. We will write a macro to a certain threshold. We will compute the probability of the wind gust exceeding 20 22 m/s ,(about 80 km/h) and generate the plot shown below:
We will compute the probabilities with a Macro in a very similar way as we did for the ensemble mean (and standard deviation). The difference is that this time we need to compute a probability for each time step.
Now duplicate the ensemble mean So create a Macro and edit it. First, read the GRIB file with the perturbed forecasts inFind the code line computing the mean and replace it with this code block:
| Code Block |
|---|
g=read("fc_pf.grib") |
Since this GRIB contains several time steps we need to write a loop to compute the probability for each time step individually. First, define the fieldset that will contain the resulting probabilities:
| Code Block |
|---|
e_prob=nil |
Next, we define the threshold for wind gust. We will store it in a variable:
| Code Block |
|---|
val=20 |
Now we can process the fields in a loop going through the time steps:
f=f > 22
f=100*mean(f) |
The first line in the code above, performs a logical operation on the fieldset and results in a new fieldset. In this new fieldset we have only 1s and 0s:
- the value is 1 in each gridpoint where the condition meets (i.e. the value is larger than the threshold)
- the value is 0 in all other gridpoints.
The second line simply derives the probability as the mean of these fields. We multiply the result by 100 to scale it into the 0-100 range for an easier interpretation.
Once you finished your Macro, visualise your Geographical View icon and drag the Macro into the plot. Customise it with the prob_shade Contouring icon. Also use a custom Text Plotting icon to define the title. As for the probabilities, you should see that there is some probability of high wind speeds.
Creating a stamp plot
In this part we will investigate the individual ENS members and create a plot showing them all for a given time step on the same page like this:
This plot, for an obvious reason, is called a stamp plot. This is a complex plot so we will write a Macro to generate it.
Create a new Macro and edit it. Drop your Geographical View and the Coastlines icons into the Macro editor. Once you've tidied up the code, define a 6x9 layout so that each plot should contain your view:
| Code Block |
|---|
dw=plot_superpage(pages: mxn_layout(my_view,9,6)) |
Next, drop your wgust_shade Contouring icon into the Macro editor and tidy up the generated code. We will apply this icon to all the fields in the stamp plot.
Continue with reading in the GRIB file of the ENS forecasts:
| Code Block |
|---|
g=read("fc_ens.grib") |
Define a variable to hold the time step we want to plot:
| Code Block |
|---|
step = 90 |
The stamp plot will be generated by plotting each perturbed forecast member into a separate map, so we need to write a loop like this:
| Code Block |
|---|
for i=1 to 50 do |
| Code Block |
tsLst=[84,90,96] loop step in tsLst ...your code will go here ... end loopfor |
Within the loop, simply read all the members current perturbed forecast member for the given timesteptime step:
| Code Block |
|---|
f=read(data: g, number: i, type: "pf", step: step ) |
then compute their mean with the mean() macro function
| Code Block |
|---|
f = mean(f) |
and add it to the resulting fieldset:
| Code Block |
|---|
e_mean = e_mean & f |
We finish the macro by returning the resulting fieldset:
| Code Block |
|---|
return e_mean |
By using the return statement our Macro behaves as if it were a fieldset (GRIB file). Drag it into the bottom left map and customise it with the wgust_shade Contouring icon and the title_mean Text Plotting icon. You will see that the ensemble mean hints that high wind speed can happen.
Part 3: ensemble members
Next, define a title. The available space for the title in the plot is confined (we need to squeeze more than 50 maps into a page!) so the title should be short:
| Code Block |
|---|
title = mtext(text_line_1 : "PF: " & i) |
Last, plot the field into the right map in our layout:
| Code Block |
|---|
plot(dw[i],title,f,wgust_shade) |
Having done so we have finished the code inside the loop. Now visualise your Macro (this will take a minute or so) and try to identify the ENS members predicting high wind speeds in our area.
Creating a spaghetti plot
We finish the case study by looking into the predictability of the large scale flow pattern by generating spaghetti plots from the same ENS run as we investigated before. In a spaghetti plot each ENS member is rendered into the same map using a single isoline value. The plot we want to generate is shown below (it contains the spaghetti plot for 500 hPa geopotential using the 560 gpm isoline value):
This is a fairly complex plot and we will write a Macro to produce itWe will create a stamp plot for a selected timestep i.e. we will plot the all the 50 ENS members.
Create a new Macro and edit it. Drop your Geographical View and the Coastlines icons into the Macro editor . Once the code is generated and tidied up define a 6x9 layout so that each plot should contain your view:
| Code Block |
|---|
dw=plot_super_page(pages: mxn_layout(my_view,9,6)) |
Next, read the GRIB file with the perturbed forecasts in:
| Code Block |
|---|
g=read("fc_pf.grib") |
Since this GRIB contains several time steps we need to write a loop to compute the probability for each time step individually. First, define the fieldset that will contain the resulting probabilities:
| Code Block |
|---|
e_prob=nil |
Next, we define the timestep we want to plot. We will store it in a variable:
| Code Block |
|---|
val=90 |
and change the map area to
| Code Block |
|---|
[40,-40,70,20] |
so that our map could show a larger (North Atlantic) area.
Next, define the contouring used for the "spaghetti" by dropping the cont_spag Contouring icon into the Macro. A code like this should be generated for you:
| Code Block |
|---|
cont_spag = mcont(
contour_label: "off",
contour_level_selection_type : "level_list",
contour_level_list : 560,
contour_line_colour: "blue",
contour_highlight: "off"
) |
In this mcont() we turned contour labels off to keep the plot uncluttered and defined only a single contour value (for 560 gpm).
Continue with reading in the GRIB file of the ENS forecasts used for the "spaghetti":
| Code Block |
|---|
g = read("spag_ens.grib") |
The "spaghetti" will be generated by plotting each perturbed forecasts member as a separate layer into the same map. To achieve this goal we need to write a loop like this:Now we will
| Code Block |
|---|
for i=1 to 50 do
...your code will go here ...
end for |
Within the loop, simply read all the perturbed forecast members for the given timestepall the time steps:
| Code Block |
|---|
f=read(data: g, steptype: step"pf", number: i ) |
then compute their mean with the mean() macro functionBy default, if no title definition is specified, Metview adds a title line for each field in the plot. Since we are about to plot 50 fields into the same map this would result in 50 titles in the plot! To avoid having too many titles we use a custom Text Plotting icon:
| Code Block |
|---|
title = mtext( text_line_1 : "member: " &i, text_font_size: 0.2 ) |
and add it to the resulting fieldset:
| Code Block |
|---|
plot(dw[i],title,f,wgust_shade) |
We finish the macro by returning the resulting fieldset:
| Code Block |
|---|
return e_mean |
Value: 560 gpm T+<grib_info key='step' where='number=50' /> h" ) |
Here we used the where statement inside the grib_info tag (as described here) to make the title appear for one member (the 50th member) only.
Last, plot the field with our contour settings and title:
| Code Block |
|---|
plot(your_view,f,cont_spag,title) |
Having done so we have finished the code inside the loop. Now visualise your Macro (it will take half a minute or so) and animate through the steps to see how the spaghetti is spreading out over time.
Extra Work if You Have Time
Add more fields to the stamp plot
The stamp plot only shows the perturbed ENS members but there is still space left to display additional fields, as well. Try to add the control forecast (from ENS) and the operational forecast to it. Some hints:
plot the control forecast into the 51st map (
dw[51]). The control forecast is stored in the same file as the perturbed forecast members: fc_ens.grib. Read it in with this code:Code Block f = read(data: g, type: "cf", step: step)plot the operational forecast into the 52nd map (
dw[52]). The operational forecast is stored in fc_oper.grib. Read it in with this code:Code Block f =read(source: "fc_oper.grib", step: step)
NOTE: While setting up these extra plots it is a good idea to temporarily comment out the loop processing the perturbed forecast members.
Add more fields to the spaghetti plot
The spaghetti plot only shows the perturbed ENS members. Try to add the control forecast (from ENS) and the operational forecast to it as well. You should use different isoline colours for them. Some hints:
use a thick red contour line. The control forecast is stored in the same file as the perturbed forecast members: spag_ens.grib. Read it in with this code:
Code Block f = read(data: g, type: "cf")
use thick green contour line. The operational forecast is stored in spag_oper.grib. Read it in with this code:
Code Block f = read("spag_oper.grib")
NOTE: While setting up these extra plots it is a good idea to temporarily comment out the loop processing the perturbed forecast membersBy using the return statement our Macro behaves as if it were a fieldset (GRIB file). Drag it into the bottom left map and customise it with the wgust_shade Contouring icon and the title_mean Text Plotting icon. You will see that the ensemble mean hints that high wind speed can happen.