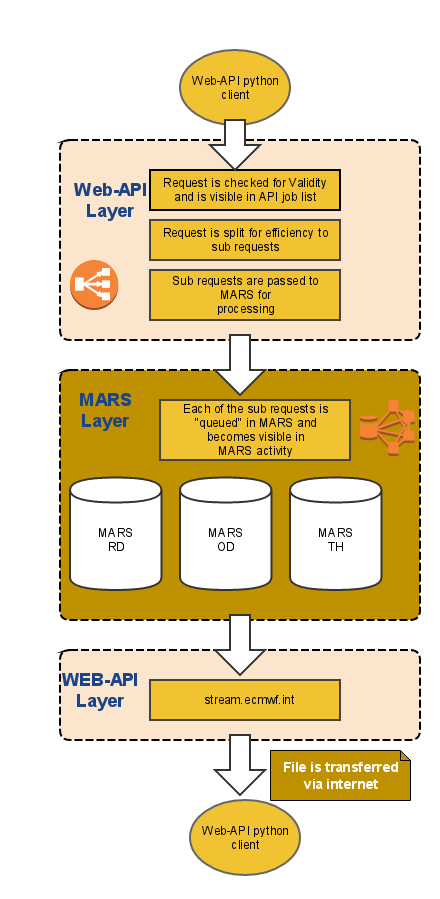
Request submitted by the user and arrives in the Web API queue
The request arrives to the service back-end and it is checked for validity.
A new request record is added in the service database. (MongoDB).
Initially, the request gets the status "queued" and it becomes visible on Web API activity
- At this phase the request is not yet visible on the MARS activity
Please note:
- If a user exceeds the maximum number of queued requests, any further requests from that user will be rejected to prevent abuse and ensure fair resource allocation.
Each request is stored as a new record in MongoDB. The corresponding record includes all the request's details (current status, timers, host, user, etc).
The request record is updated periodically to reflect its current status.
The web-API client is checking the current status periodically via an http status check (the service is asyncronous)
The "queue time" depends on several factors, eg priorities, limitations, current load, etc
Please note that to improve the service some QoS limitations and priorities are applied, on both the webAPI and MARS like:
The total maximum number of active requests
The maximum number of active requests per user
- The maximum number of queued requests per user
- etc
Once an API slot is available and all the QoS rules are met, the request will become "active" on the Web API level.
The request becomes active on Web API level
Split: On the Web-AP, I level, the request is split into a number of smaller requests to achieve better performance from the MARS point of view. For instance, if a request is asking for one year of S2S daily data, it is split per month. ie it is split into 12 requests.
Validate: Each of these sub-requests are passed to a MARS client running on one of the available web hosts.
The request becomes active on MARS level
Initially, the request becomes "queued" on the level of MARS and it is visible on the MARS activity
- Once a MARS slot is available and if all the MARS QoS rules are met, the request will become "active" on the MARS level.
- Note that a request can be at status "active" on the level of API but "queued" on MARS.
On the level of MARS server, there are several MARS QoS rules (ie limitations, restrictions and priorities) like the ones below.
On marsod-core, the total number of Requests from ECMWF Web API with 1 tape mount [source] is limited to 6
On marsth-core, the total number of Requests from ECMWF Web API with 1 tape mount [source] is limited to 12
To avoid long queuing times it is strongly recommended to improve your Retrieval efficiency
The request is completed or aborted
Once all the sub-requests have completed successfully the corresponding sub-files are merged into a final one and the request status becomes complete
If something goes wrong during the procedure above the request status will get the value "aborted"
File transfer procedure
If the request is completed succesfully, the produced data is then transferred by the Web API client to the user's local disk (target file).
Once the data transfer is completed, the initial file will be removed from the ECMWF systems and it won't be any more available.
If the transfer procedure fails
The file transfer procedure may fail due to several reasons (eg network connectivity problems between our end and the users)
The API client checks the volume of the transferred file and if the size is not the expected one the transfer procedure will start again. The MAX number of retries is 10
- If the transfer is not successful, the user may be able to manually download it from the Job List.