...
Although ECMWF has used both systematic and case study analyses to document the most significant and substantial changes for users, the list below can not be considered exhaustive - other features may well come to light in the coming months.
On 11th October some new text was added to this web page, shown in green. Some additional figures were also added nearby.
...
Precipitation
A large set of cases in different "synoptic type" categories where precipitation tends to occur were examined; these included orographic rainfall (convective, large-scale, mix), cold fronts, warm fronts, diurnal convection over land, SST-triggered convection, tropical convection, MCSs (mesoscale convective systems). In almost all of these classes the precipitation rate patterns look to be systematically different in 47r3.
...
"Mixed picture" means marked regional variations. The maximum change at any location in any of these classes is about 15%.
Regional average changes, over summer and winter seasons, at a 48-hour lead time, are illustrated on the following plot (Warm warm colours mean more cloud in 47r3).
...
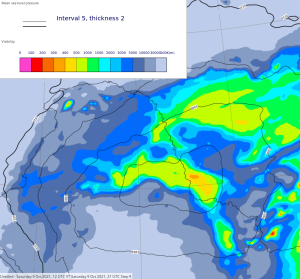
The following panels compare visibility in an October case over northernmost China with snow and rain. 47r3 looks much more realistic with in showing lower values overall in the snow than in the rain; the opposite was seen in 47r2.
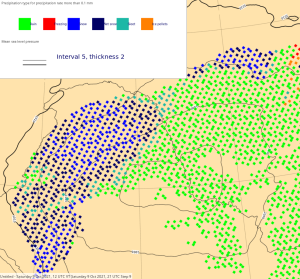
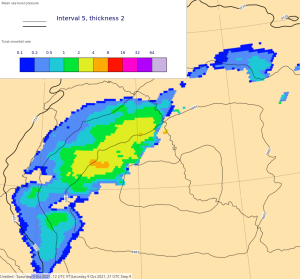
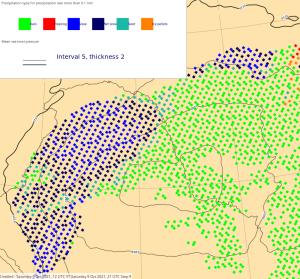
| Diagnosed Ppn type | Total Precipitation Rate | Total Snowfall Rate | Visibility | |
47r2 (old cycle) | ||||
47r3 (new cycle) |
...
Wind gusts
The 10m wind gust parametrisation has been changed in two ways in cycle 47r3; the first change reduces the standard 'turbulent gusts' by 7%, the second change reduces the convective gust addition by 50% (whenever it is applied). The net result is slightly lower gusts overall, albeit with the size of the impact depending on the situation.
...