In this tutorial we will demonstrate This tutorial demonstrates how to run a forward simulation with FLEXPART and how to visualise the results in various ways.
| Expand | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
|
| Note |
|---|
Please enter folder ' |
...
forward' to start working. |
Running the simulation
...
| Info |
|---|
In this tutorial we will run a forward simulation by releasing some SO2 from the Icelandic volcano Eyjafjallajökull. |
The simulation itself is defined by the 'fwd_conc' FLEXPART Run icon and the 'rel_volcano' FLEXPART Release icon, respectively. Both these are encompassed in a single macro called 'fwfwd_condconc.mv'. For simplicity will use this macro to examine the settings in detail.
...
This says that the release will happen over a 45 h period between heights 1651 and 10000 m at the location of the volcano and we will release 1000 tons of material in total.
| Info |
|---|
Please note that
|
The actual simulation is carried out by calling flexpart_run():
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
#Run flexpart (asynchronous call!)
r = flexpart_run(
output_path : "result_fwd_conc",
input_path : "../data",
starting_date : 20120517,
starting_time : 12,
ending_date : 20120519,
ending_time : 12,
output_field_type : "concentrationconc",
output_flux : "on",
output_trajectory : "on",
output_area : [40,-25,66,10],
output_grid : [0.25,0.25],
output_levels : [500,1000,2000,3000,4000,5000,7500,6000,7000,8000,9000,10000,11000,12000,13000,14000,15000],
release_species : 8,
releases receptors : "on"rel_volcano,
receptor_names release_units : ["rec1","rec2mass"],
receptor_latitudes units : [60,56.9],
receptor_longitudes : [6.43,-3.5],
releases : rel_volcano
"mass"
)
print(r) |
Here we defined both the input and output path paths and specified the simulation period, the output grid and levels as well. We also told FLEXPART to generate gridded mass concentration and flux fields and plume trajectories on output..
| Info |
|---|
The actual species that will be released is to release are defined as an integer number (for details about using the species see here). With the default species settings number 8 stands for SO2. |
If we run this macro (or alternatively right-click execute the FLEXPART Run icon) the results (after a minute or so) will be available in folder 'result_fw_concfwd'. The computations were actually taken took place in a temporary folder then metview Metview copied the results to the output folder. If we open this older folder 'result_fwd' we will see two three files there:
- conc_s001.grib is a GRIB file containing the gridded concentration fields
- trflux_r1s001.csv grib is CSV a GRIB file containing the plume trajectoriesgridded flux fields
- log.txt is the log file generated by FLEXPART
| Info |
|---|
Please note that these are not the original outputs form |
...
FLEXPART but were converted to |
...
more suitable ones for |
...
Metview. For details about the FLEXPART outputs |
...
click here. |
Visualising gridded fields
To plot a particular parameter and level we need to filter the desired dataset from the resulting FLEXPART output file. Unfortunately, Metview's Grib Filter icon cannot handle these files (partly due to the local GRIB definition they use) so we need to use other means to cope with this task. For this reason and also to make FLEXPART output handling easier a set of Metview Macro Library Functions were developed. We will heavily use these functions in the examples below.
Inspecting the FLEXPART GRIB file
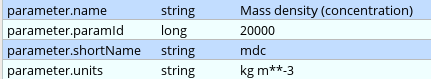
Before seeing the macro code to generate the plot we inspect the file itself we wanted to plot. Double-click on the 'conc_s001.grib' GRIB icon' in folder 'result_fw_conc' to start up the Grib Examiner. We can see that this file only contains "mdc" (=Mass density concentration) fields. We can find out further details about this parameter by setting the Dump mode to Namespace and Namespace to Parameter:
Generating the plot
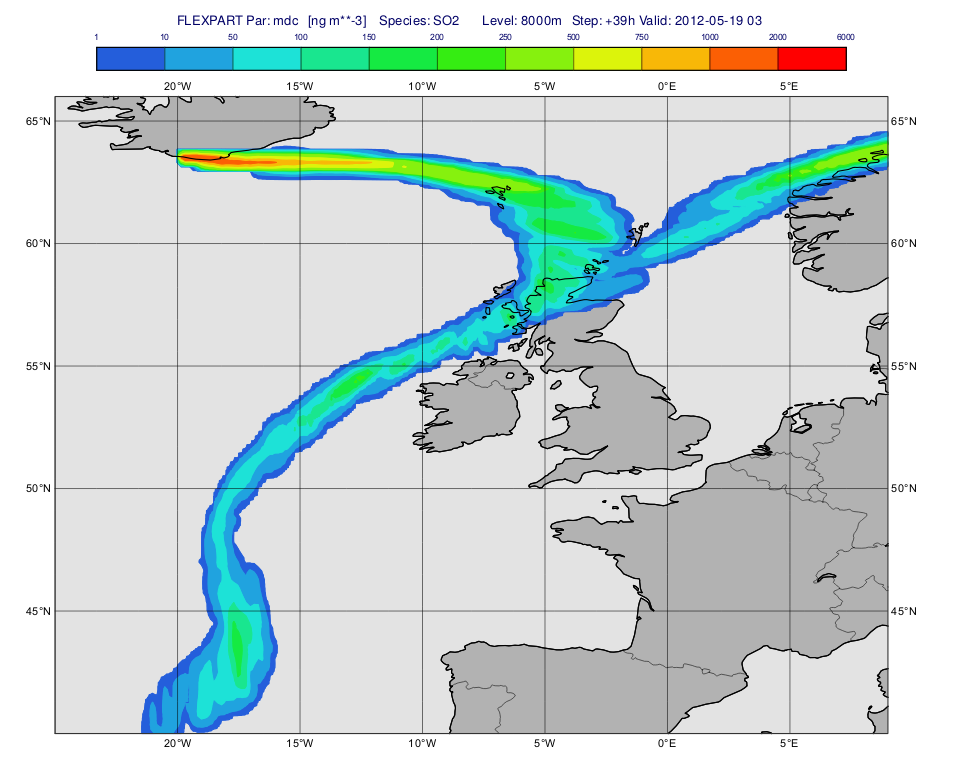
The macro to visualise the concentration fields on a given level is 'plot_level.mv'.
First, we define the level (8000 m) and the parameter ("mdc") we want to plot. Then we call mvl_flexpart_read_hl() to filter the data into a fieldset.
| Code Block |
|---|
dIn="result_fwd_conc/"
inFile=dIn & "conc_s001.grib"
lev=8000
par="mdc"
#Read fields on the given height level
g=mvl_flexpart_read_hl(inFile,par,lev,-1,-1) |
Next, we define the contouring definition. The units we used here are ng m**-3 because for parameter "mdc" the native units (kg m**-3) are automatically scaled by the plotting library (see details about the this scaling for various FLEXPART GRIB fields here.
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
#The contour levels
cont_list=[1,10,50,100,150,200,250,500,750,1000,2000,6000]
#Define contour shading
conc_shade = mcont(
legend : "on",
contour : "off",
contour_level_selection_type : "level_list",
contour_level_list : cont_list,
contour_label : "off",
contour_shade : "on",
contour_shade_method : "area_fill",
contour_shade_max_level_colour : "red",
contour_shade_min_level_colour : "RGB(0.14,0.37,0.86)",
contour_shade_colour_direction : "clockwise",
contour_method: "linear"
) |
Next, we build the title with mvl_flexpart_title(). Please note that we need to explicitly specify the plotting units!
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
title=mvl_flexpart_title(g,0.3,"ng m**-3") |
Finally we define the view with the map:
| Code Block | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
#Define coastlines
coast_grey = mcoast(
map_coastline_thickness : 2,
map_coastline_land_shade : "on",
map_coastline_land_shade_colour : "grey",
map_coastline_sea_shade : "on",
map_coastline_sea_shade_colour : "RGB(0.89,0.89,0.89)",
map_boundaries : "on",
map_boundaries_colour : "black",
map_grid_latitude_increment : 5,
map_grid_longitude_increment : 5
)
#Define geo view
view = geoview(
map_area_definition : "corners",
area : [40,-25,66,9],
coastlines: coast_grey
) |
and generate the plot:
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
plot(view,g,conc_shade,title) |
Having run the macro we get a plot like this (after navigating to step 39h):
Computing and plotting total column mass
The macro to visualise the concentration fields on a given level is 'plot_total.mv'.
First, we define the level (8000 m) and the parameter ("mdc") we want to plot. Then we call mvl_flexpart_read_hl() to filter the data into a fieldset.
| Code Block |
|---|
dIn="result_fwd_conc/"
inFile=dIn & "conc_s001.grib"
lev=8000
par="mdc"
#Read fields on the given height level
g=mvl_flexpart_read_hl(inFile,par,lev,-1,-1) |
To process and visualise the results please see these pages:
| Children Display |
|---|